Alternate Exterior Angles
Alternate exterior angles definition
Alternate exterior angles are created when three lines intersect. A line that crosses two or more other lines is called a transversal. Often, two of the lines will be parallel, setting up some interesting angles with the transversal.
When a transversal crosses two other lines, it creates an exterior and interior for the parallel lines. Alternate exterior angles are created in the space outside the parallel lines on alternating sides; interior angles are created in the space inside the parallel lines.
Here are lines TR and IP, which would definitely cross somewhere in the distance. We cut across TR and IP with transversal SW, and where the transversal crosses TR and IP, we have Points L and O. Yep, it's a SLOW TRIP.
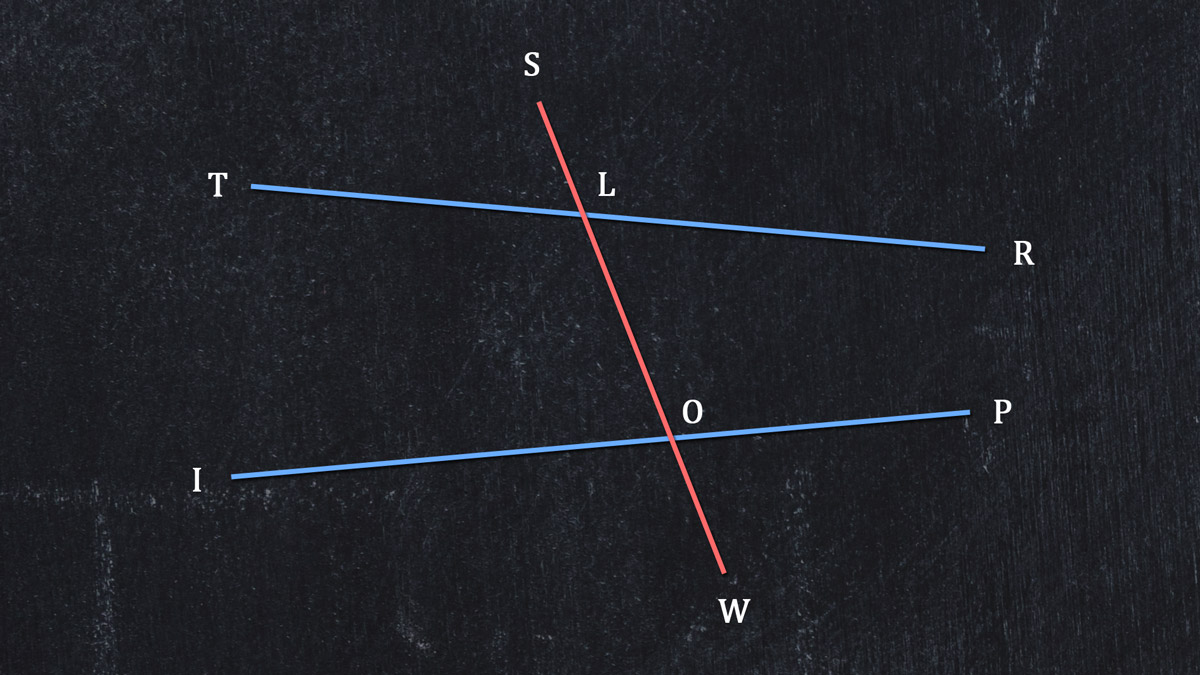
We can write each angle with three letters: ∠SLT, ∠SLR, and so on down to ∠POW.
We can also use numbers in these same vertices, so ∠SLT is 1, ∠SLR is 2, and so on, ending with ∠POW as 8.
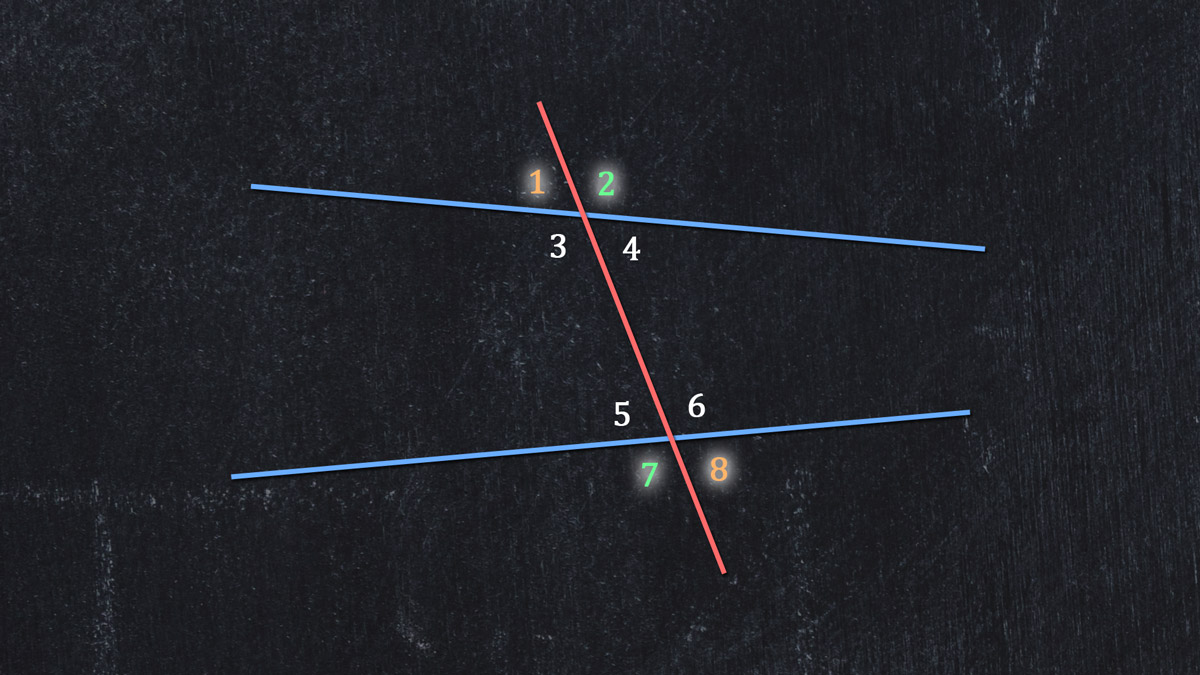
The four exterior angles:
∠1
∠2
∠7
∠8
Alternate exterior angles are pairs that appear outside the crossed lines and on different lines:
∠1 and ∠8
∠2 and ∠7
Alternate exterior angles theorem
When two lines are parallel, the transversal creates congruent alternate exterior angles. The Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem states that if a pair of parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the alternate exterior angles are congruent.
Here we have a new pair of lines, parallel and crossed by a transversal. We are not bothering to identify our parallel lines and transversal! We are jumping ahead to numbered angles.
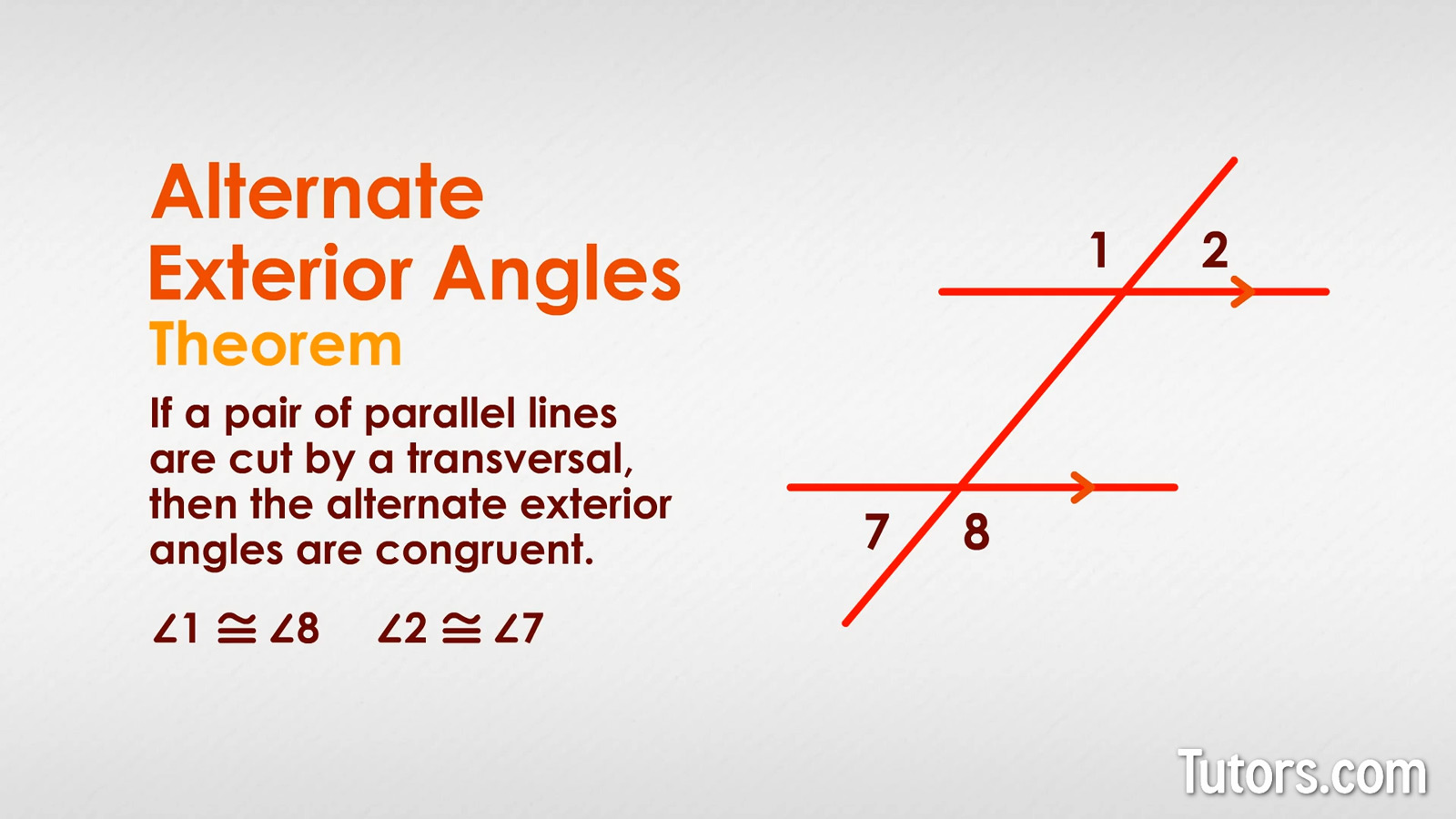
The exterior angles are these same four:
∠1
∠2
∠7
∠8
This time, we can use the Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem to state that the alternate exterior angles are congruent:
∠1 ≅ ∠8
∠2 ≅ ∠7
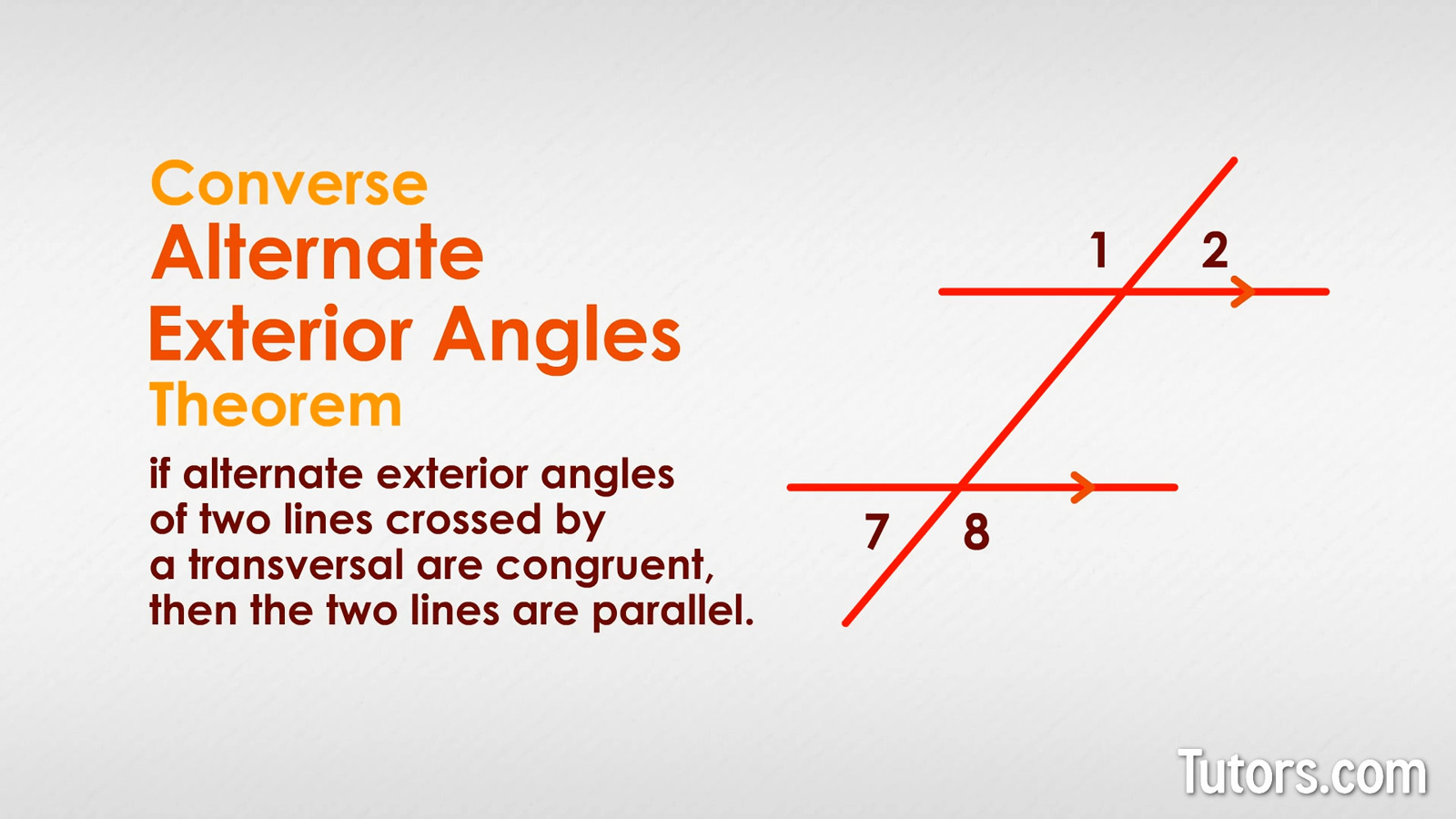
Converse of the alternate exterior angles theorem
The converse of the Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem is also true. The converse of the Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem states that if alternate exterior angles of two lines crossed by a transversal are congruent, then the two lines are parallel.
Alternate exterior angles examples
Begin by identifying alternate exterior angles, a common geometry problem. Here is another set of lines crossed by a transversal, with numbered angles:
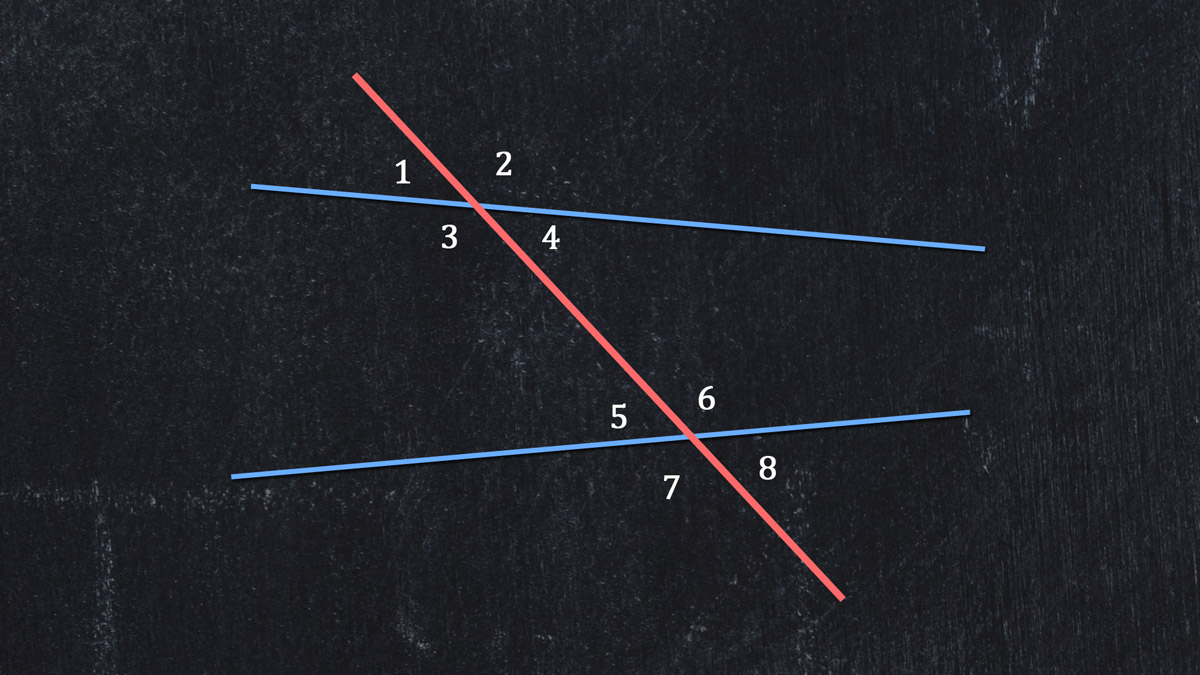
Which are exterior angles?
Which are alternate exterior angles?
To find exterior angles, look in the space above and below the crossed lines. To find alternate exterior angles, look at that outside space for each crossed line, on different sides of the transversal.
We hope you said ∠1, ∠2, ∠7, and ∠8 are the exterior angles. We also hope you identified ∠1 and ∠8 as a pair of alternate exterior angles and ∠2 with ∠7 as the other pair.
Another type of problem is to identify the other angle that pairs with a given alternate exterior angle. Here are more lines and a transversal, with numbered angles:
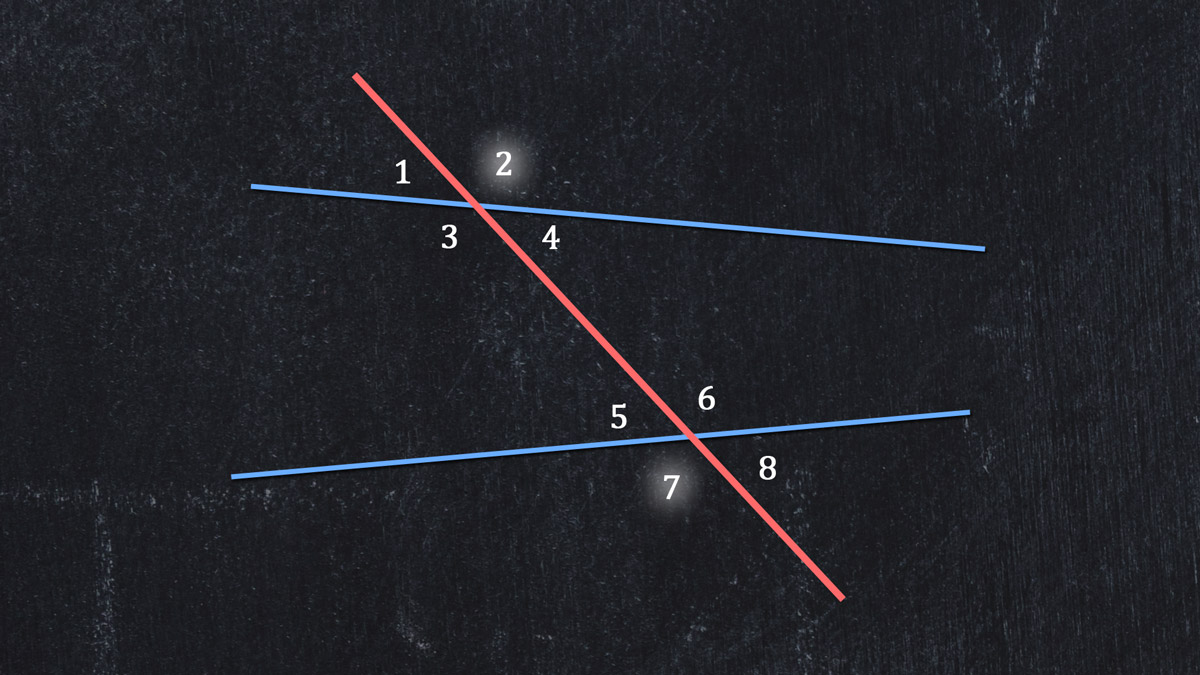
To find the partner of ∠2, look on the other side of the transversal. Look outside the crossed lines. Look at a crossed line that does not contain ∠2.
Did you say ∠7? We hope so!
Example with parallel lines
Here is a drawing with parallel lines and a transversal.
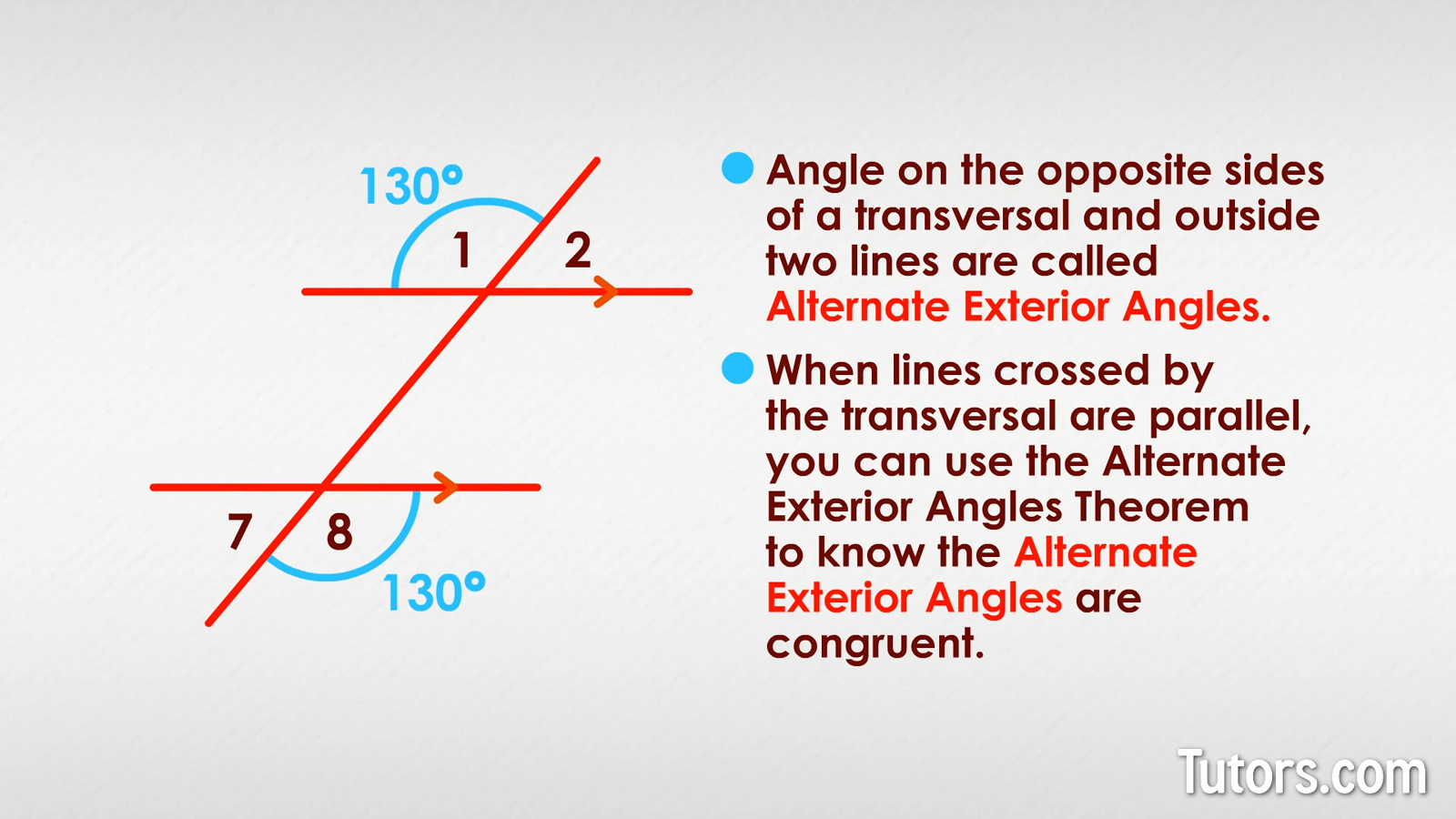
If we know that ∠8 measures 130°, what is the measure of ∠1?
∠8 is on the outside of the bottom parallel line, and to the right of the transversal. That means ∠1 is its alternate exterior angle partner. The Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem tells us it is also 130°!
Lesson summary
Now that you have gone through this lesson carefully, you are able to recall that angles on opposite sides of a transversal and outside two lines are called alternate exterior angles.
When lines crossed by the transversal are parallel, you can use the Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem to know the alternate exterior angles are congruent. You can now solve problems identifying and measuring alternate exterior angles.
Geometry is a bit like a magician's trick. It sets up some odd event, like parallel lines being crossed by a transversal, and then hopes you're astounded when that improbable event leads to something new, like alternate exterior angles.
Even when the lines are not parallel, alternate exterior angles exist, and we don't need to pull a rabbit out of a hat to amaze you with them.