What Is a Polygon?
Polygon definition
A polygon is a plane figure that closes in a space using only line segments. If it must use only line segments and must close in a space, the polygon with the fewest sides has to be the triangle (three sides and interior angles).
Polygon; the word means "many angles," but it ignores one attribute: straight sides. Polygons are all around us! Learning about these basic plane shapes helps you understand geometry.

Let's look at how many sides each polygon has:
Polygons have no upper limit to the number of sides and interior angles, so mathematicians say n-gon after the familiar names we use for common polygons.
| Polygon Shape | Number of Sides |
|---|---|
| Triangle | 3 sides |
| Square | 4 sides |
| Rectangle | 4 sides |
| Quadrilateral | 4 sides |
| Parallelogram | 4 sides |
| Rhombus | 4 sides |
| Dart | 4 sides |
| Kite | 4 sides |
| Pentagon | 5 sides |
| Hexagon | 6 sides |
| Heptagon | 7 sides |
| Octagon | 8 sides |
| Nonagon | 9 sides |
| Decagon | 10 sides |
| Dodecagon | 12 sides |
| Icosagon | 20 sides |
| Hectagon | 100 sides |
| n-gon | n sides |
Polygon shapes
Let's take a look at the vast array of shapes that are polygons.
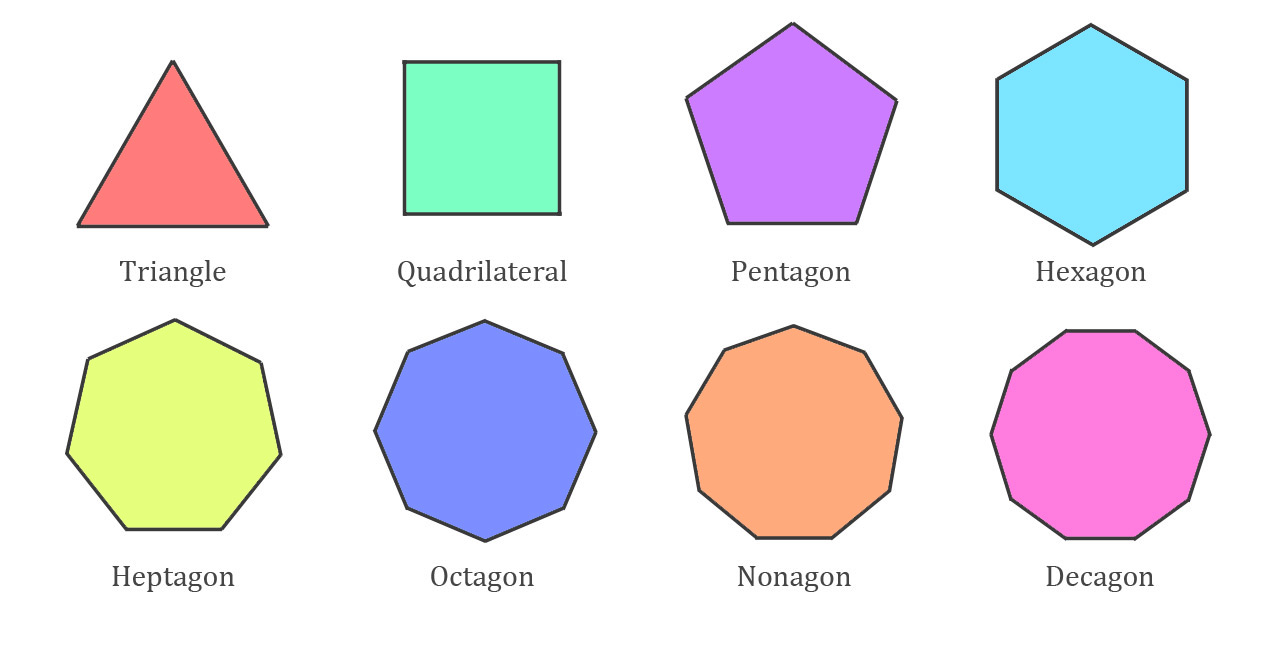
Types of polygons
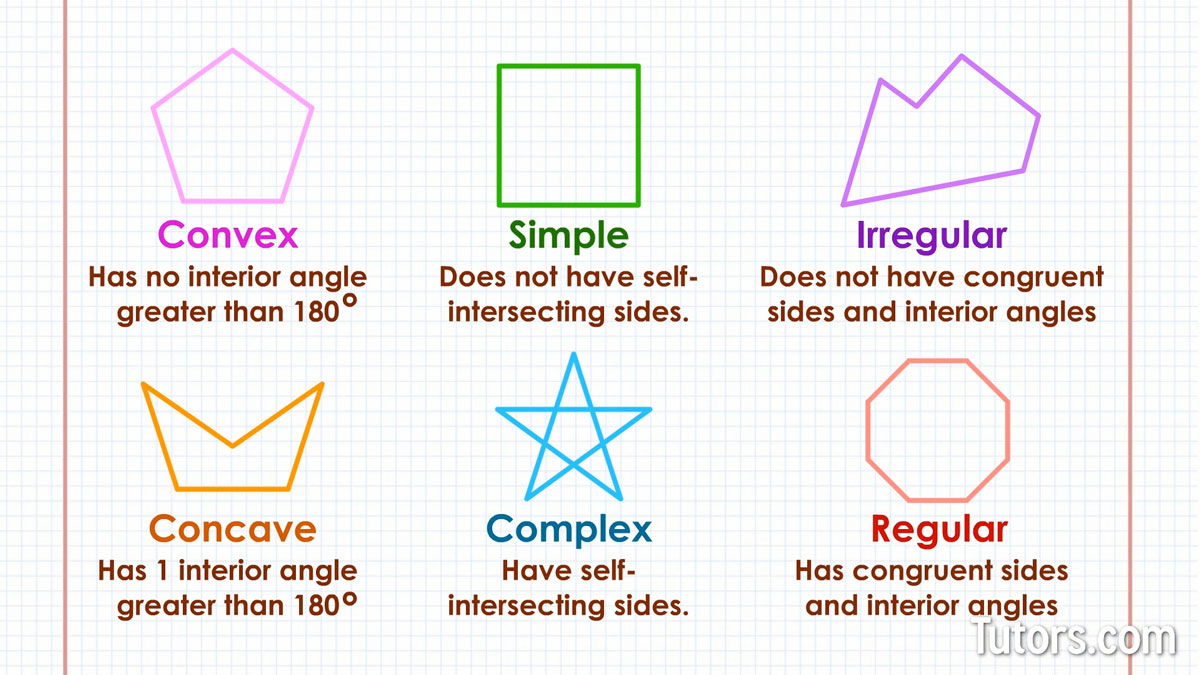
A convex polygon has no interior angle greater than 180° (it has no inward-pointing sides). A concave polygon has one interior angle greater than 180°.
A simple polygon encloses a single interior space (boundary) and does not have self-intersecting sides. Complex polygons have self-intersecting sides!
An irregular polygon does not have congruent sides and interior angles.
A regular polygon has congruent sides and interior angles.
Regular polygons
Let's take a closer look at regular polygons. A regular polygon is where all sides are the same length, and all angles are also all the same. Next time you're in a car, take a closer look at a stop sign. A stop sign is an example of a regular polygon with eight equal sides.

Types of regular polygons
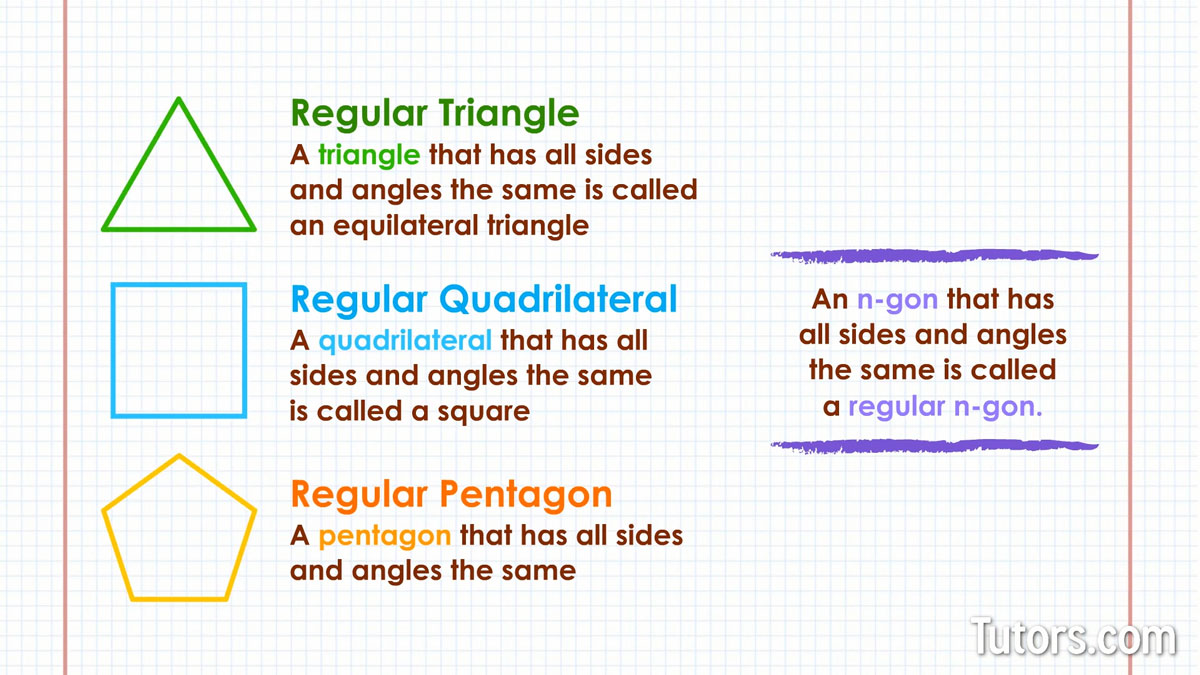
A triangle that has all sides and angles the same is called an equilateral triangle, or regular triangle.
A quadrilateral that has all sides and angles the same is called a square, or regular quadrilateral.
A pentagon that has all sides and angles the same is known as a regular pentagon.
An n-gon that has all sides and angles the same is called a regular n-gon.
Check out these regular polygons. Do you notice how all the sides and angles are the same no matter how you flip it?
Interior angles of polygons
The interior angles of polygons are the vertices, or inside corners, created by endpoints of line segments.
Connecting all the vertices inside a simple polygon without crossing any lines creates triangles.
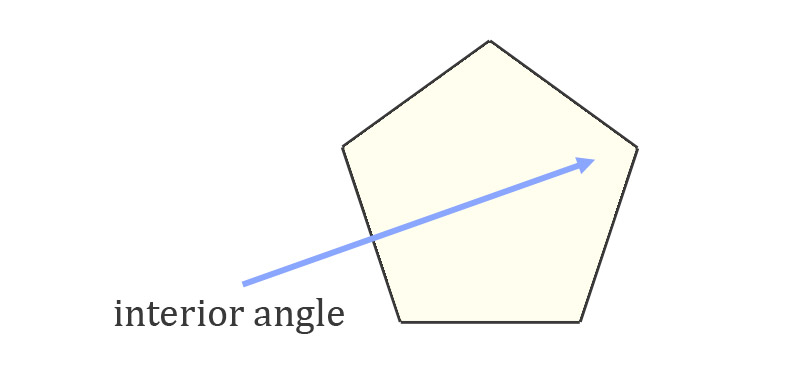
Finding the sum of interior angles
Each triangle adds to 180°, so one way to find the sum of interior angles is to count the number of dividing triangles:
Triangle (1 triangle); 180°
Quadrilateral (2 triangles); 180°× 2 = 360°
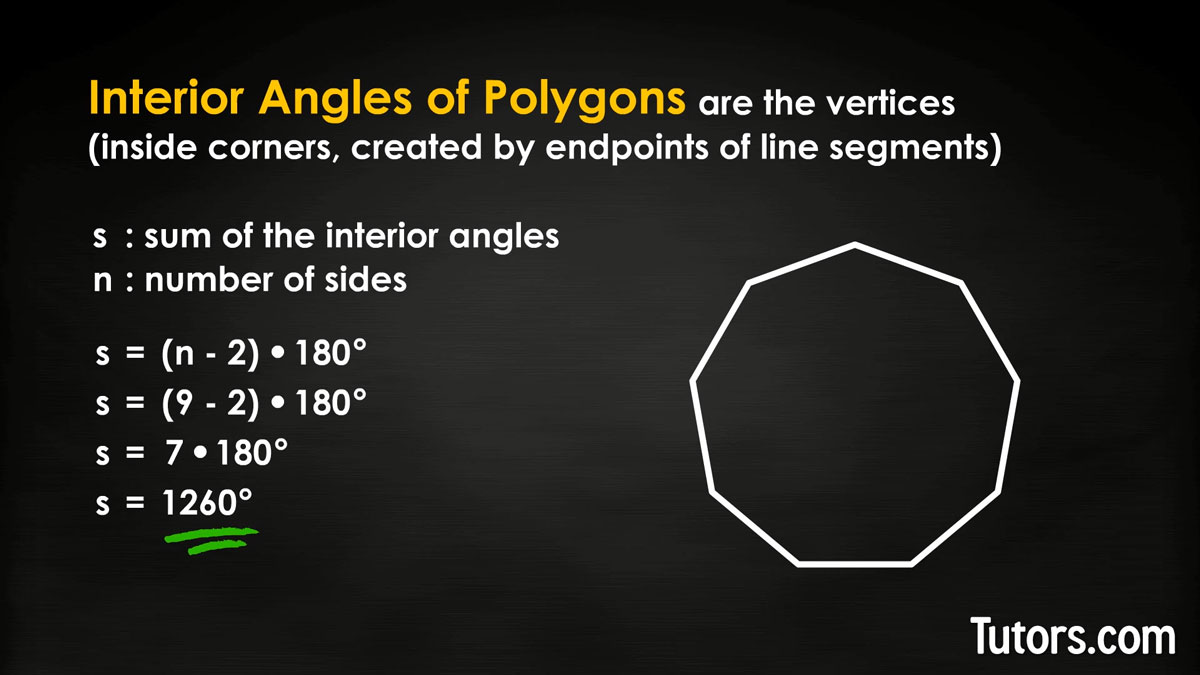
Nonagon (7 triangles); 180°× 7 = 1260°
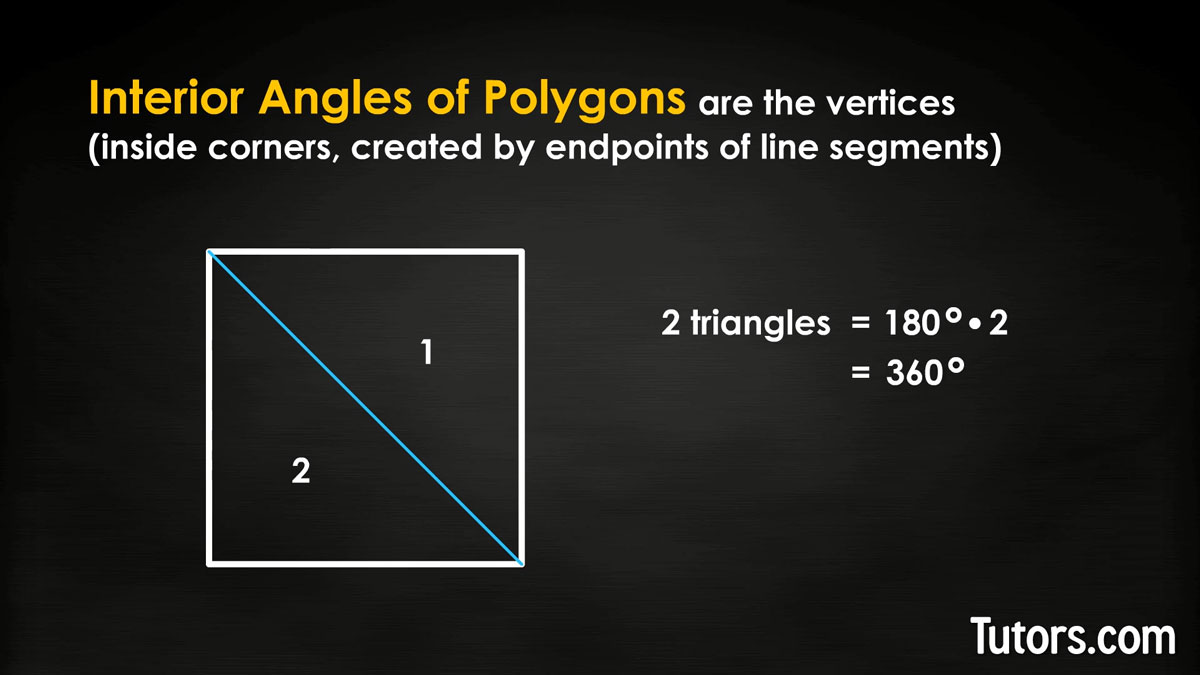
That can get clumsy after a while. You can instead use a formula for the sum ss of the interior angles. You need to know the number of sides n:
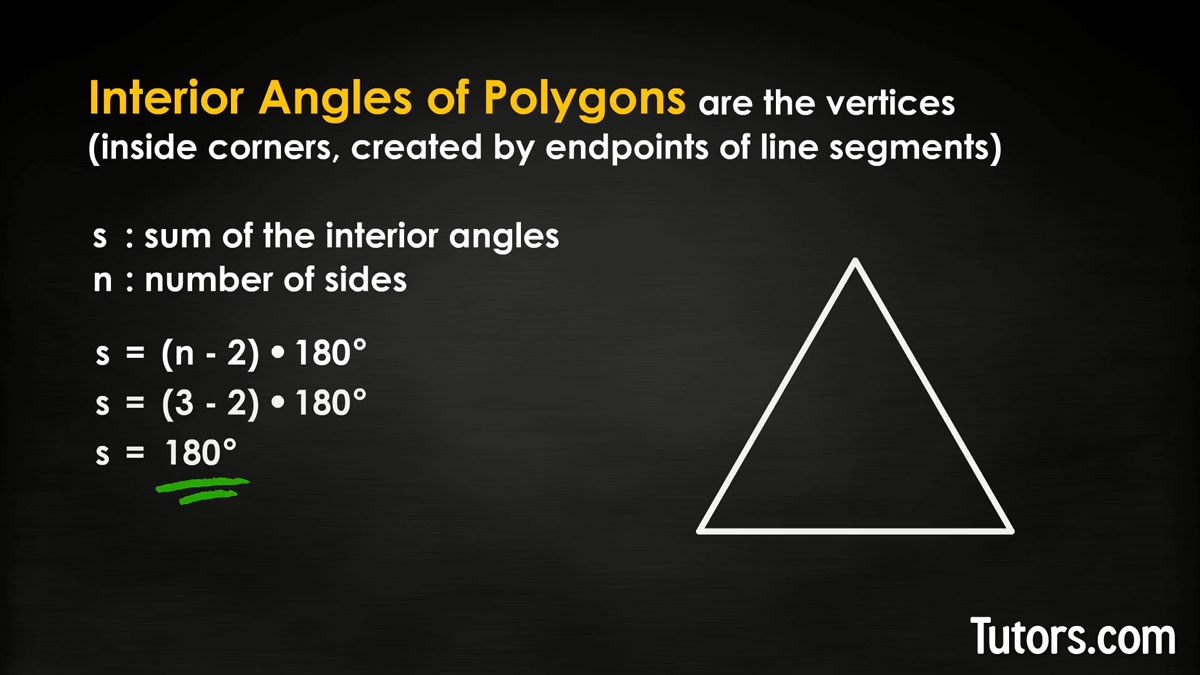
Sum of interior angles of a triangle
Try it yourself, on a triangle:
Sum of interior angles of a nonagon
Now try it on a nonagon, a nine-sided polygon:
Interior angles of regular polygons
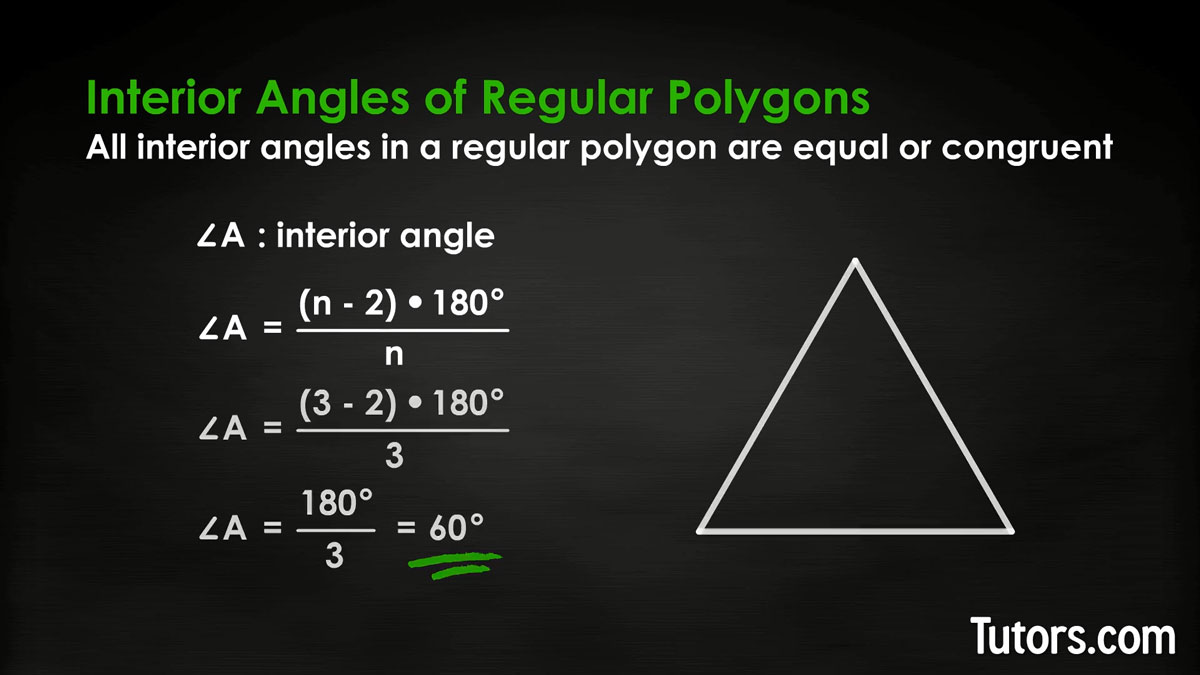
All interior angles in a regular polygon are equal (interior angles are congruent). Once you know how to find the sum of interior angles, you can use that to find the measure of any interior angle, ∠A, of a regular polygon. Take the same formula and divide by the number of sides:
Triangle
Let's try it out for an equilateral triangle by plugging in 3 for the number of sides (n):
Nonagon
Here is a regular nonagon (9 sides):
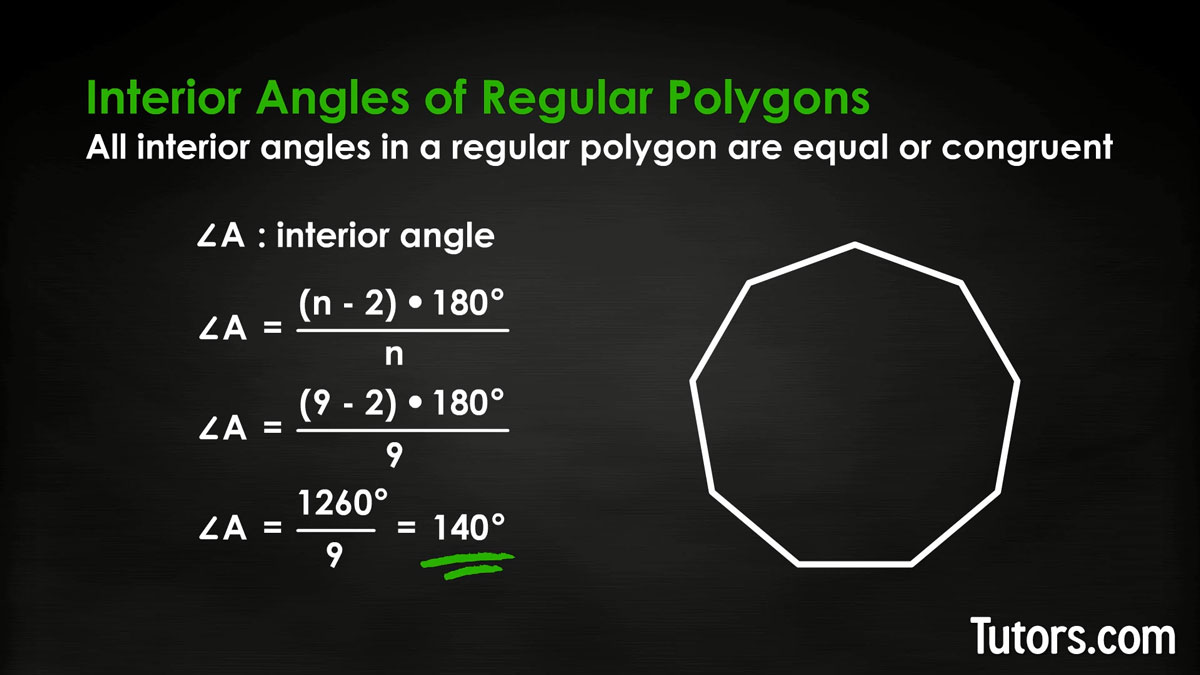
The formula can be rearranged like this:
Both versions will give you the same answer. Notice the second part of that version of the formula, . We are going to use that next!
Exterior angles of polygons
The number of interior angles and exterior angles of any polygon is the same. A triangle has three exterior angles; a square has four; our nonagon has nine.
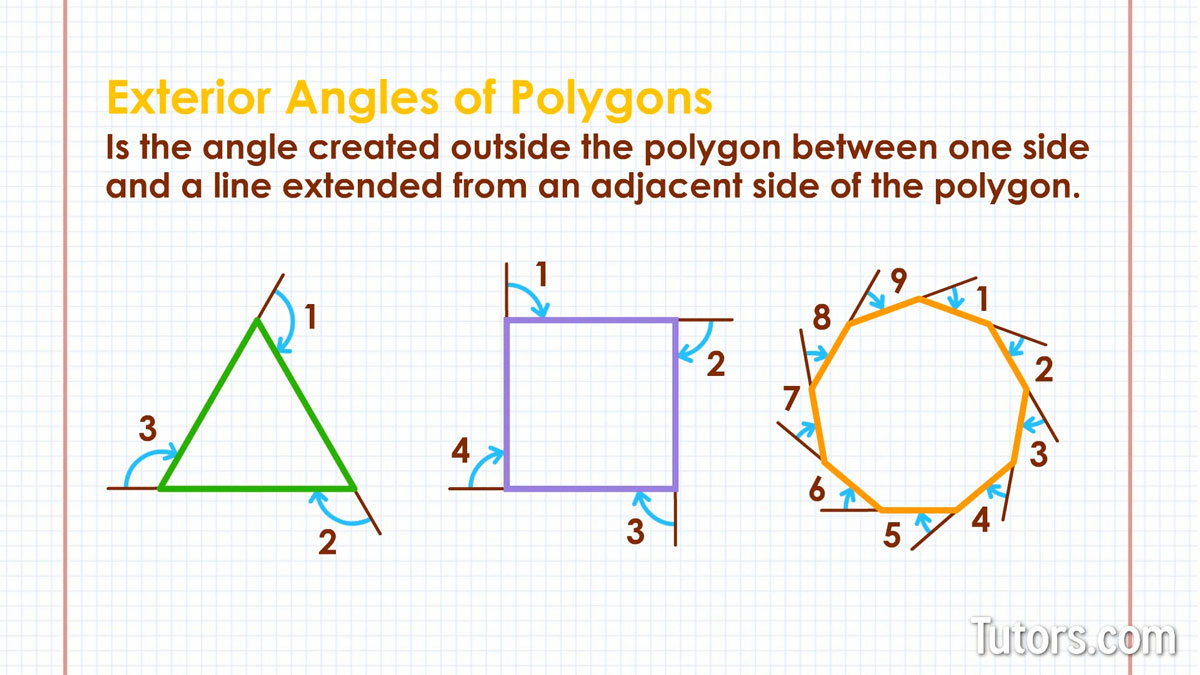
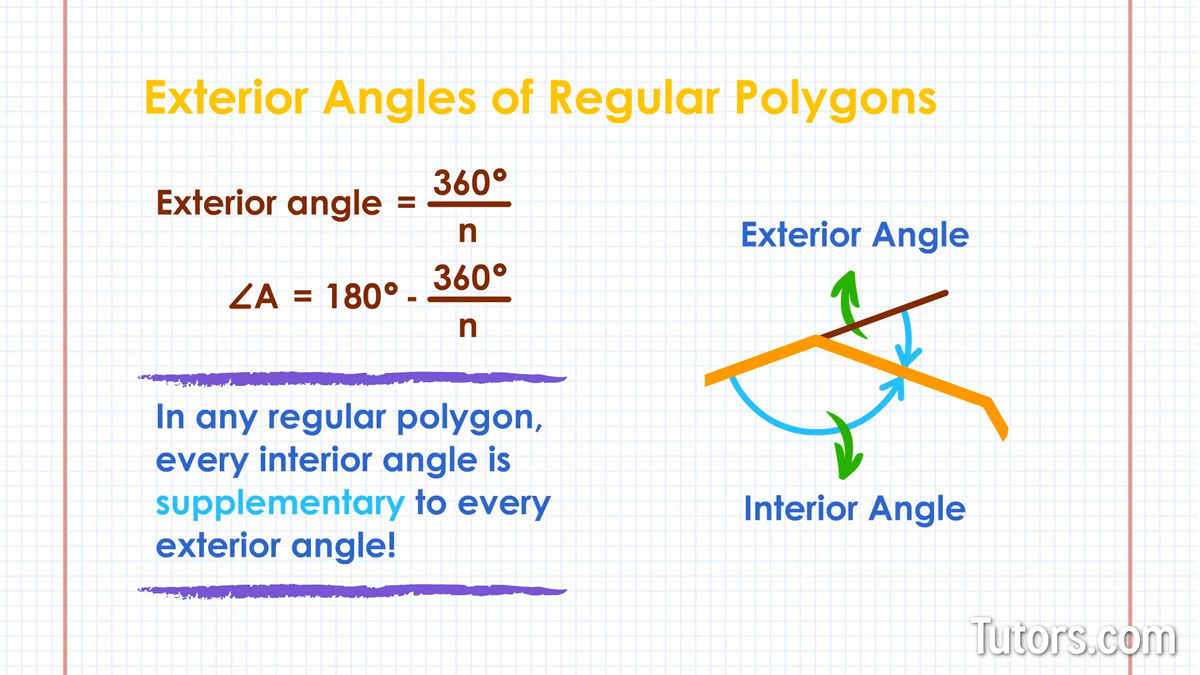
An exterior angle is an angle created outside the polygon between one side and a line extended from an adjacent side of the polygon. The interior and exterior angles will always add to 180°, so they are supplementary.
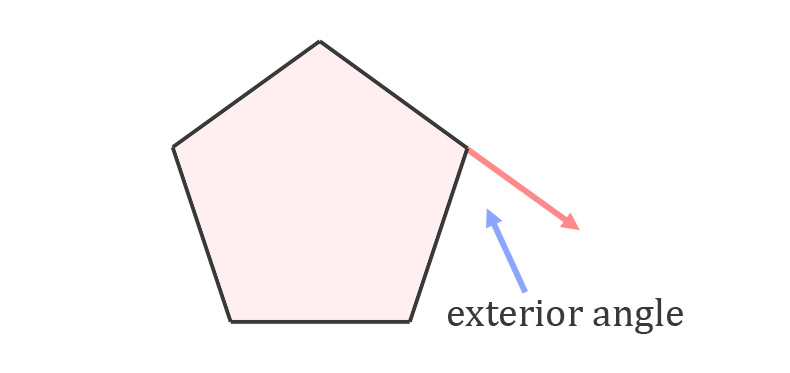
On irregular polygons, you have no way of knowing the measure of exterior angles. On regular polygons with n sides, you can use a formula to know each of the shape's exterior angles, since they will be congruent:
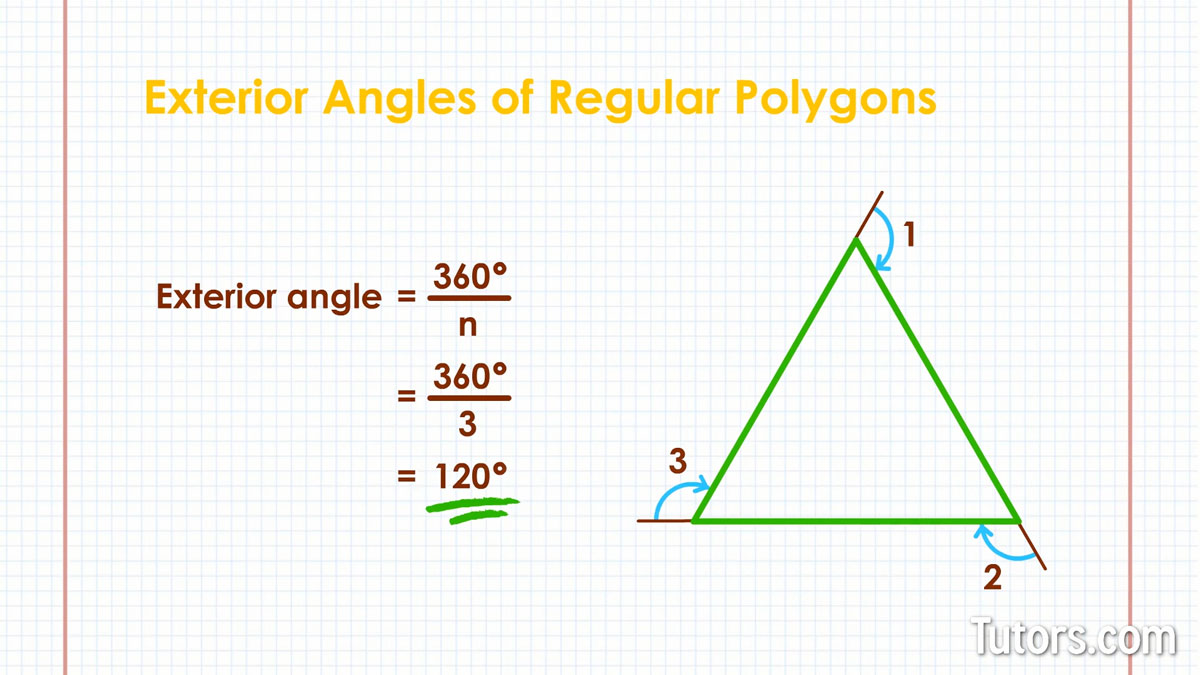
Exterior angles of a triangle
In an equilateral triangle, the exterior angles come out like this:
Exterior angles of a nonagon
Our nonagon does this:
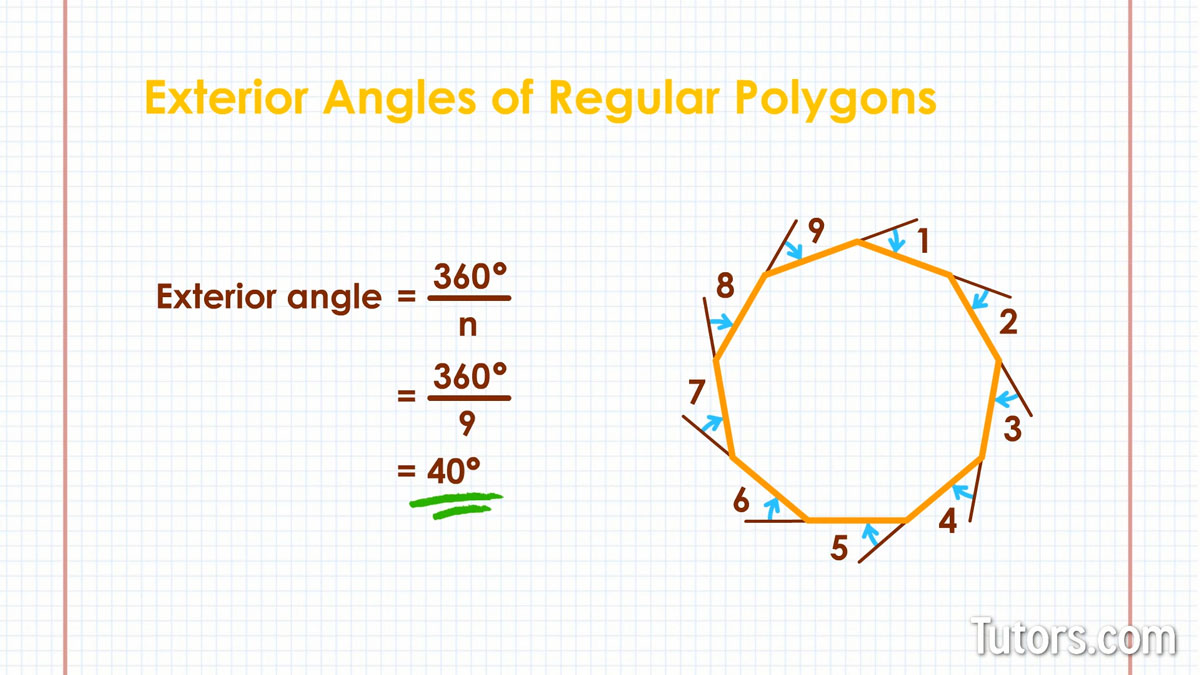
A regular n-gon does this:
Look back at the second version of the formula for finding interior angles of regular polygons, which we wrote as:
Now you can see that the two formulas make sense together because one finds the supplementary angle of the other.
Lesson summary
You should now be able to identify and define both a polygon and regular polygon, find the sum of the interior angles of regular and irregular polygons, and find the interior and exterior angles of any regular polygon.
You can use formulas to find the sum of interior angles for any polygon and to know the exact measure of both interior and exterior angles for regular polygons.