Equations Of A Circle | Standard & General Form
Circle on a graph
Circles are everywhere, and every circle can be described mathematically by either of two formulas. The first takes advantage of the Pythagorean Theorem. The second formula applies either the standard form or general form for the equation. We will look at both formulas.
When you consider a circle on a coordinate graph is the set of all points equidistant from a center point, you can see that those points can be described as an (x, y) value on the graph. Move right or left so many boxes (that's the x value), and then move up or down to the y value.
With the circle's center point also an (x, y) value, you can create a right triangle with the two sides x boxes left or right from that center point, and y boxes up or down from that same center point.
The radius, r, of the circle -- the distance from the center point to the circle itself -- now becomes the hypotenuse for every possible right triangle for every possible point.
A circle has infinite points, since points are dimensionless positions in space. So, at least in the pure science of mathematics, an infinite number of right triangles exist that satisfy and every one of them has a vertex (of the hypotenuse and one side of the triangle) lying on the circle.
How to find the equation of a circle
Imagine a circular orbit of a satellite around Mars.
We never want the satellite to hit Mars, but we do want to be close enough to "see" Martian features with radar, cameras, magnetometers, and lasers.
To stay in one spot above a hypothetically spherical Mars (geostationary orbit), you need an orbital radius of 20,428 kilometers.
Equation of a circle formula
If the center of Mars -- the core of the planet -- is (0, 0) on a graph, our x values extend outward from the core, while our y values extend at right angles to those x values. Our hypotenuse of every right triangle must be 20,428 km, and our circular orbit can be calculated as .
You can isolate either the x or y value to find the other. Plugging in any particular value for x will return a value for y, and all (x, y) values will fall on the satellite's orbital path.
Say you are an orbital mechanics engineer. You know your c value, your hypotenuse, is 20,428 km. You want to see the longer leg value (the y value) for a short-leg value (the x value) of 10,000 km:
Standard form equation of a circle
Orbits are one thing; circles that are not centered at (0, 0) are another. What do we do if, say, the center point of a circle on a graph is at (4, 7) instead of (0, 0)?
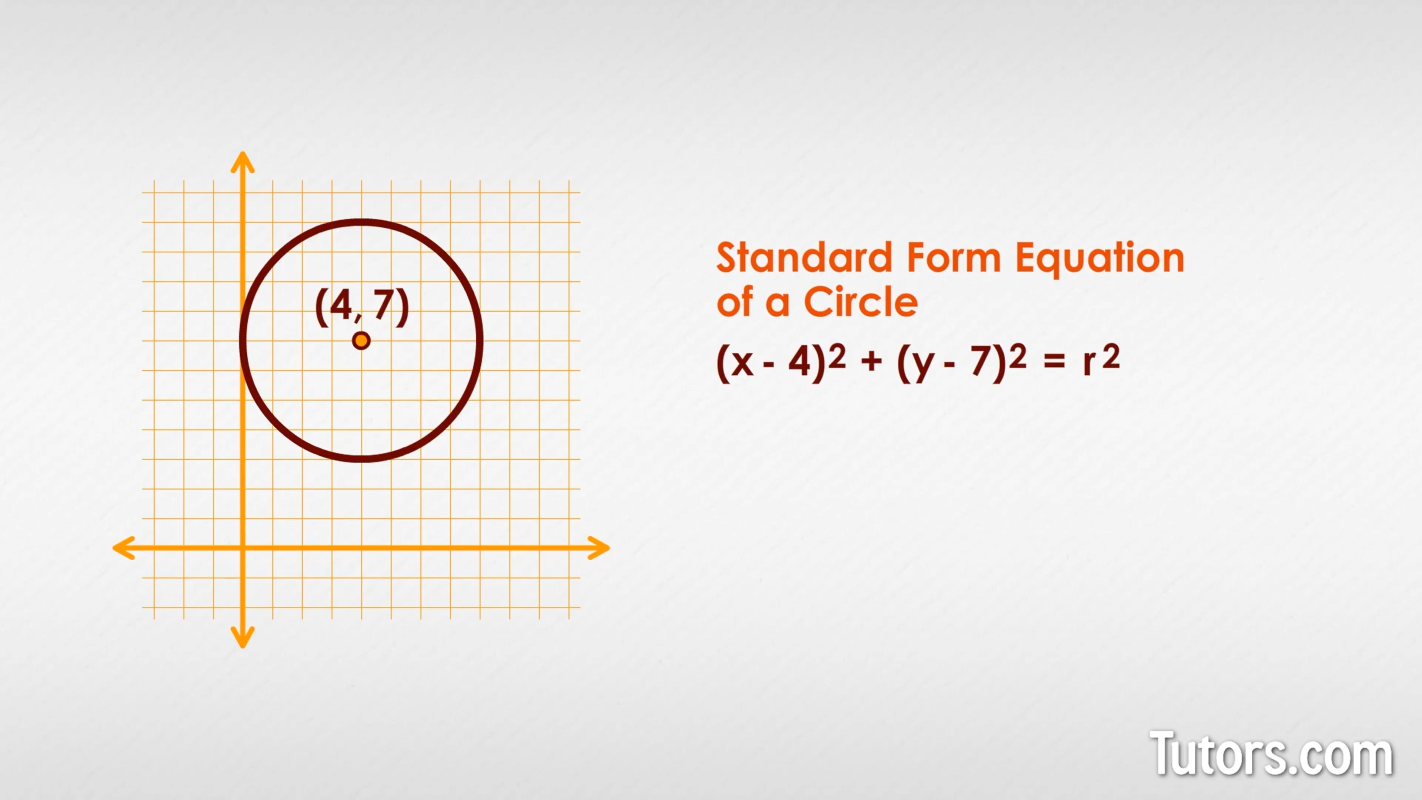
We need to compensate for this circle that "slipped away" from (0, 0), so we subtract the x-value and y-value from our original formula:
This will work even when the (x, y) coordinates are negative:
The Standard Form of a circle is that expression we just derived from the Pythagorean Theorem! We cannot use (x, y) for all the graph points, so we use other letters to identify the coordinates of the center of the circle, in this case (a, b):
From the Standard Form you have the (a, b) value to find the center point. We have our radius r. We can graph the circle.
General form equation of a circle
We can also use algebra to rearrange the equation to the General Form of a circle. This is not intuitive, so let's plug in some (a, b) and r values:
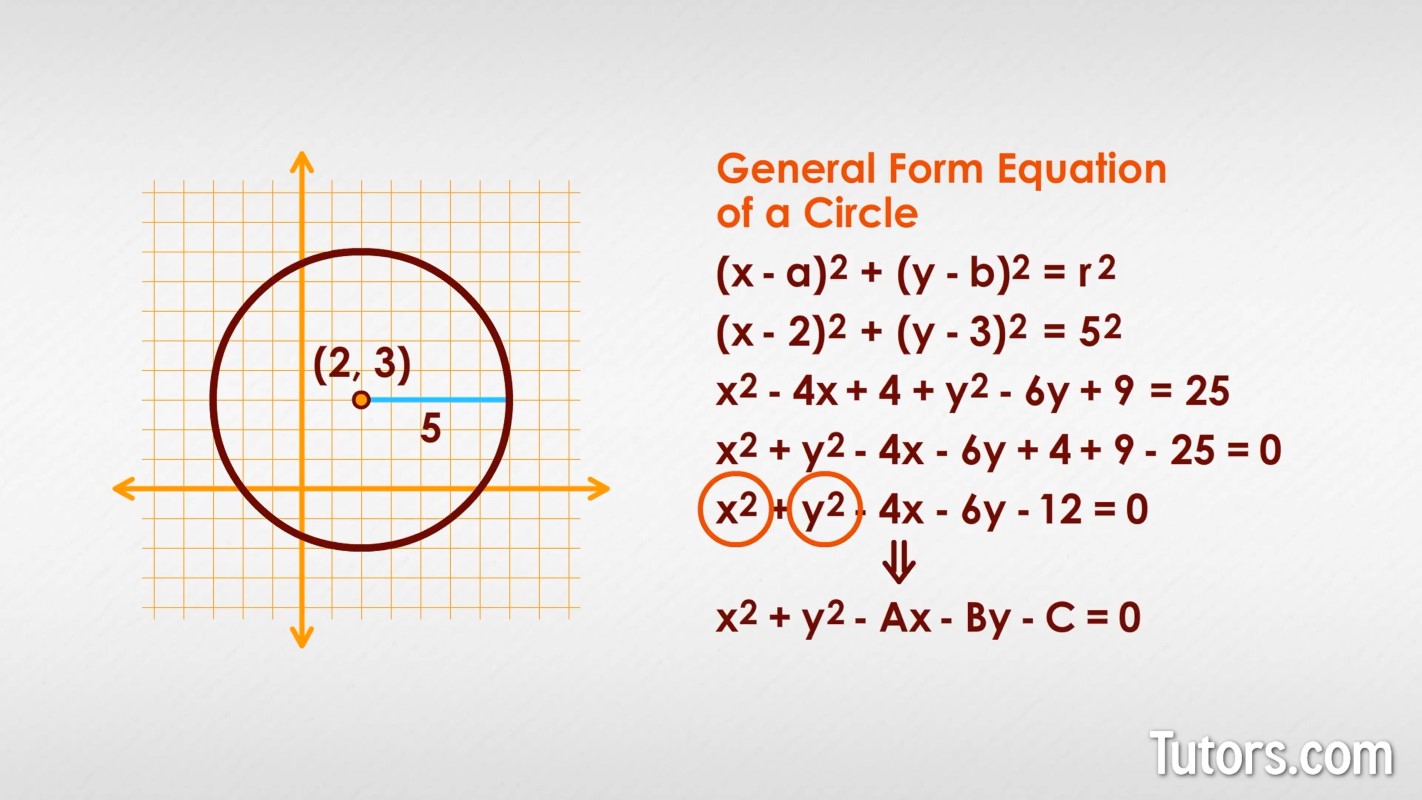
Let's expand that so you can more easily see how it turns into the General Form:
Pull like terms together, set the equation equal to 0, and we have this:
This is the General Form of a circle. You can recognize it because the two leading terms will always be and . The generic General Form Equation looks like this:
Equation of a circle examples
Choose between Standard Form and General Form based on the information you have in the problem. Having two ways to solve the equation of a circle -- using Pythagoras, or the Standard or General Forms -- gives you power.
Here is some information about a circle. Which method will you choose?
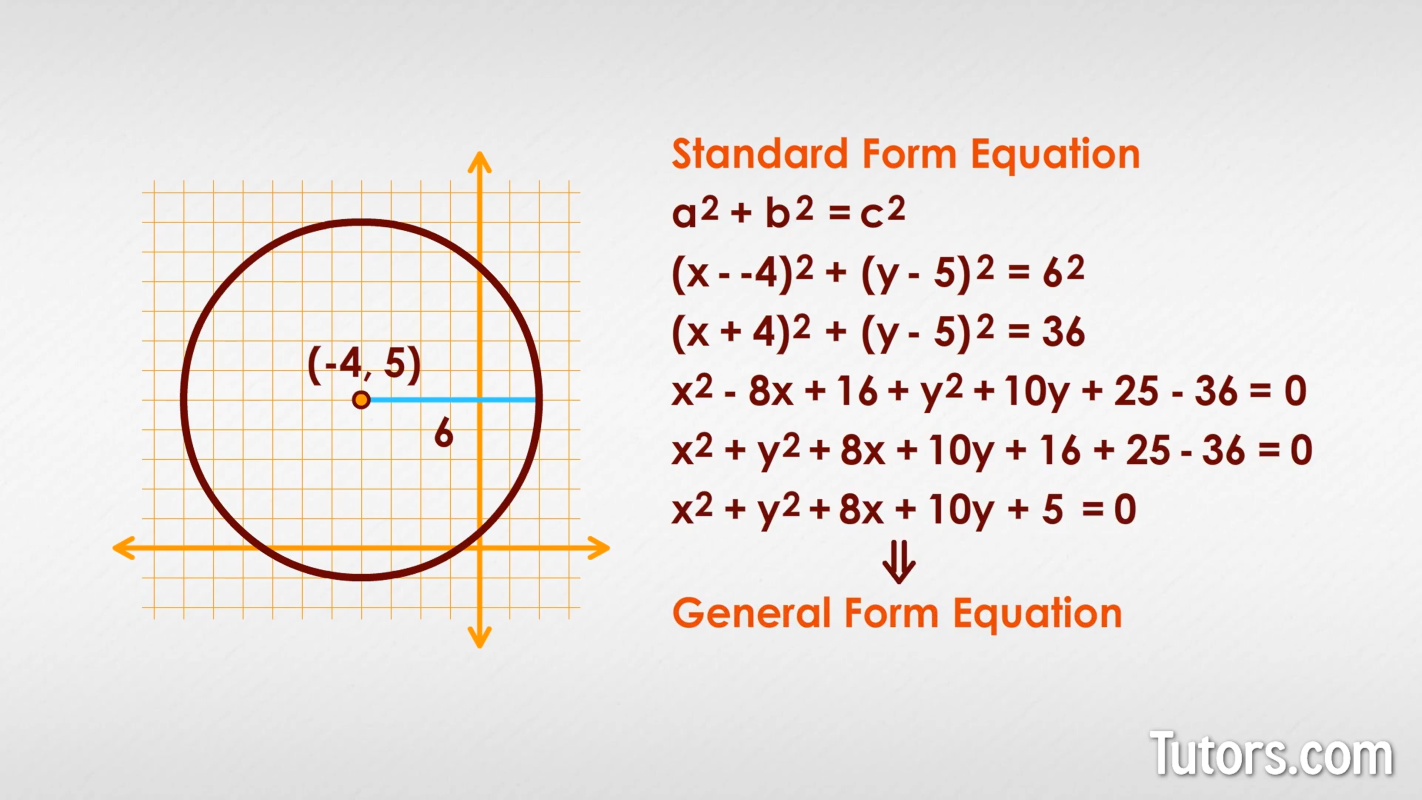
We know the center (−4, 5) and the radius, r = 6. Start with the Standard Form, which is really just a derivation of the Pythagorean Theorem :
Expand and set it to equal 0:
Combine like terms:
Simplify:
That is the General Form of the equation, derived from the Standard Form, which derives from the Pythagorean Theorem!